Ladies, have you contemplated the implications of contraceptive implants on your menstrual cycle? As an increasing number of women opt for this birth control method, comprehending its potential effects on our health is imperative. These effects may range from lighter or irregular periods to complete halting of menstruation.
If you are planning on getting an implant or have one already but are encountering menstrual symptoms, our article aims for you to have an understanding of the connection between contraceptives and menstrual cycles.
Overview of Contraceptive Implants
Contraceptive implants are a form of long-acting reversible contraception which involves inserting a small, flexible rod under the skin of the upper arm. These implants release a steady dose of the hormone progestin, which prevents pregnancy by thickening cervical mucus to block sperm and by inhibiting ovulation.
A common side effect of contraceptive implants is a change in menstrual patterns.
How Do Contraceptive Implants Affect Menstrual Patterns?
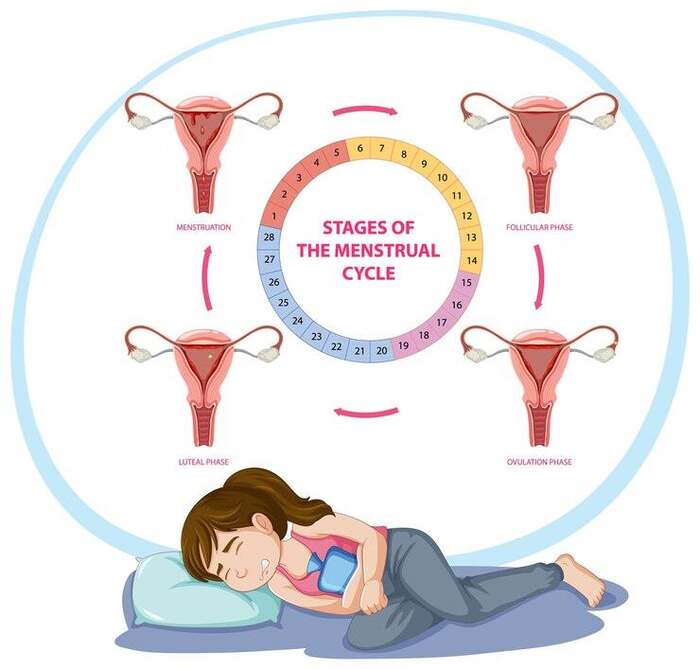
A menstrual pattern refers to the regularity, frequency, flow, and duration of menstrual cycles that a woman experiences. Typically, a normal menstrual cycle is about 28 days long, although it can range from 21 to 35 days in adults. During a normal menstrual cycle, the period—lasting between 3 to 7 days—occurs in the first phase of the cycle, followed by the follicular, ovulation, and luteal phases.
However, with contraceptive implants, the menstrual patterns may be affected.
Changes in Menstrual Frequency
You may notice a shift in your menstrual frequency; either more frequent periods or cycles become more spaced apart. These changes occur due to the hormonal alterations caused by the implant, which can suppress your ovulation or alter the regular rhythm of your menstrual cycles.
Alteration in Flow and Duration
Due to the hormonal effects of the implant, you may also find your periods becoming lighter and shorter in duration or heavier and longer menstrual bleeding. These changes result from the hormonal effects of the implant, which can thin the uterine lining or cause it to shed irregularly.
Irregular Periods or Spotting
The hormonal impact of the implant can disrupt the regular cyclical shedding of the uterus lining. You might experience unexpected bleeding or spotting between regular periods.
Potential for Amenorrhea
Amenorrhea, the complete absence of menstrual periods, is another potential outcome for women using contraceptive implants. The continuous release of hormones from the implant can suppress the menstrual cycle to the extent that periods stop altogether.
Heavy or Prolonged Bleeding
The hormonal changes introduced by the implant can increase the blood flow and lengthen the duration of menstrual bleeding.
Return to Normal after Removal
After the removal of a contraceptive implant, most women’s menstrual patterns typically return to their pre-implant once the hormonal influence of the implant dissipates. This reversion can take a few weeks to a few months.
The impact of contraceptive implants on menstrual patterns can vary widely among women. Understanding these changes can help you manage expectations and seek appropriate medical advice when necessary.
Managing Menstrual Patterns with Contraceptive Implants

With how contraceptive implants might affect your menstrual patterns, you can manage them in various ways.
Understand the Potential Changes
Understanding the possible changes in your menstrual patterns can help you adjust more effectively and reduce anxiety.
Monitor Your Menstrual Cycle
Keep track of your menstrual cycle to see how your body is responding to the implant. Use a calendar or an app to note the frequency, duration, and type of bleeding.
Stay Prepared
Irregular periods can catch you off guard. Always keep menstrual products like pads, tampons, or menstrual cups handy.
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A balanced diet, regular exercise (yoga or meditation), and proper hydration can contribute positively to your overall well-being and help manage menstrual changes.
Manage Symptoms
Some women might experience side effects like cramping or headaches. Over-the-counter pain relief medications, applying heat pads, or doing in gentle physical activity can help alleviate these symptoms.
Note: Consult your healthcare provider before taking medication.
Be Patient
Adjusting to the changes brought on by contraceptive implants can take time. Give your body a few months to adapt to the new hormonal levels before making any decisions.
Communicate with Your Healthcare Provider
Maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider, especially if you experience concerning symptoms or if the changes in your menstrual cycle are bothersome. They can offer guidance or alternative solutions tailored to your needs.
Why Do Women Choose Contraceptive Implants?
Contraceptive implants are highly effective, with a success rate exceeding 99%, and they can provide protection against pregnancy for up to three to five years, depending on the type of implant.
One of the major advantages of contraceptive implants is their convenience. Once inserted, they require no daily attention, making them an attractive option for those who may struggle with complying with a daily pill regimen. Additionally, they are discreet, and fertility typically returns rapidly after the removal of the implant.
Conclusion
While contraceptive implants offer a reliable and convenient method of birth control, they can significantly impact menstrual patterns. Being informed about these potential changes can help you manage expectations and better adapt to the new hormonal environment. Constant communication with your healthcare provider assures you that the contraceptive method aligns with your health needs and lifestyle preferences. By understanding and managing these changes, you can make empowered decisions about your reproductive health.


